The Power of Semantic Mapping in Patent Analysis
Keeping ahead of the curve when it comes to innovation strategy and research can be tricky, and understanding the intricacies of technologies, trends, and competitive landscapes is crucial for effective IP strategy and management. One popular technique that R&D teams use to navigate this landscape is known as semantic mapping. The Minesoft team have put together this article to help you understand this method of patent analysis, describing what it is and how it’s reshaping the field of patents and IP.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Semantic Mapping
- Using Semantic Mapping to Create an IP Strategy
- Semantic Mapping Example
- Best Practices for Semantic Mapping
- The Future Implications of Machine Learning & NLP
- Make Semantic Mapping Easy with Minesoft
Understanding Semantic Mapping
In the context of patents and intellectual property (IP), semantic mapping refers to the process of analysing the semantic meaning or language used in patent documentation to identify similarities, differences, and relationships between certain IP assets.
Semantic mapping for patent analysis involves using natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning techniques to understand and categorise the content of patents based on their textual descriptions, protections, claims, and other relevant information.
Using Semantic Mapping to Create an IP Strategy
In today’s rapidly evolving landscape of innovation, creating a strong IP strategy is essential for staying ahead of the competition. Semantic mapping plays a crucial role in this process by providing valuable insights into the vast universe of patents and IP assets. Let’s explore how semantic mapping can be leveraged to help craft a robust IP strategy:
Patent Landscaping
Patent landscaping involves mapping out the competitive landscape within a specific technology domain or industry. Semantic mapping allows R&D teams to visualise this landscape by identifying clusters of patents related to a particular technology or development. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of existing patents and their relationships, companies can identify emerging trends, key players, and potential areas for innovation or licensing.
Prior Art Search
Conducting a thorough prior art search is essential before filing a patent application and helping you pass patentability assessments with flying colours by ensuring the novelty and nonobviousness of an invention.
Semantic mapping enhances the efficiency of this process by analysing the semantic content of patents to identify relevant prior art. By leveraging NLP and machine learning techniques, R&D teams can uncover patents with similar concepts or technologies, thereby reducing the risk of patent infringement and increasing the chances of a successful patent application process.
Technology Scouting & Competitive Intelligence
Semantic mapping enables companies to scout emerging technologies and gather competitive intelligence by analysing the semantic content of patents. By identifying trends, innovative approaches, and competitor activities, organisations can make informed decisions about R&D investments, strategic partnerships, and potential licensing opportunities.
Portfolio Management
Effective portfolio management is essential for maximising the value of intellectual property assets. Semantic mapping facilitates portfolio analysis by organising patents into meaningful clusters based on their semantic content. This allows companies to identify strengths, weaknesses, and gaps within their portfolio, optimise resource allocation, and make strategic decisions regarding patent acquisition, licensing, or divestiture.
Semantic Mapping Example
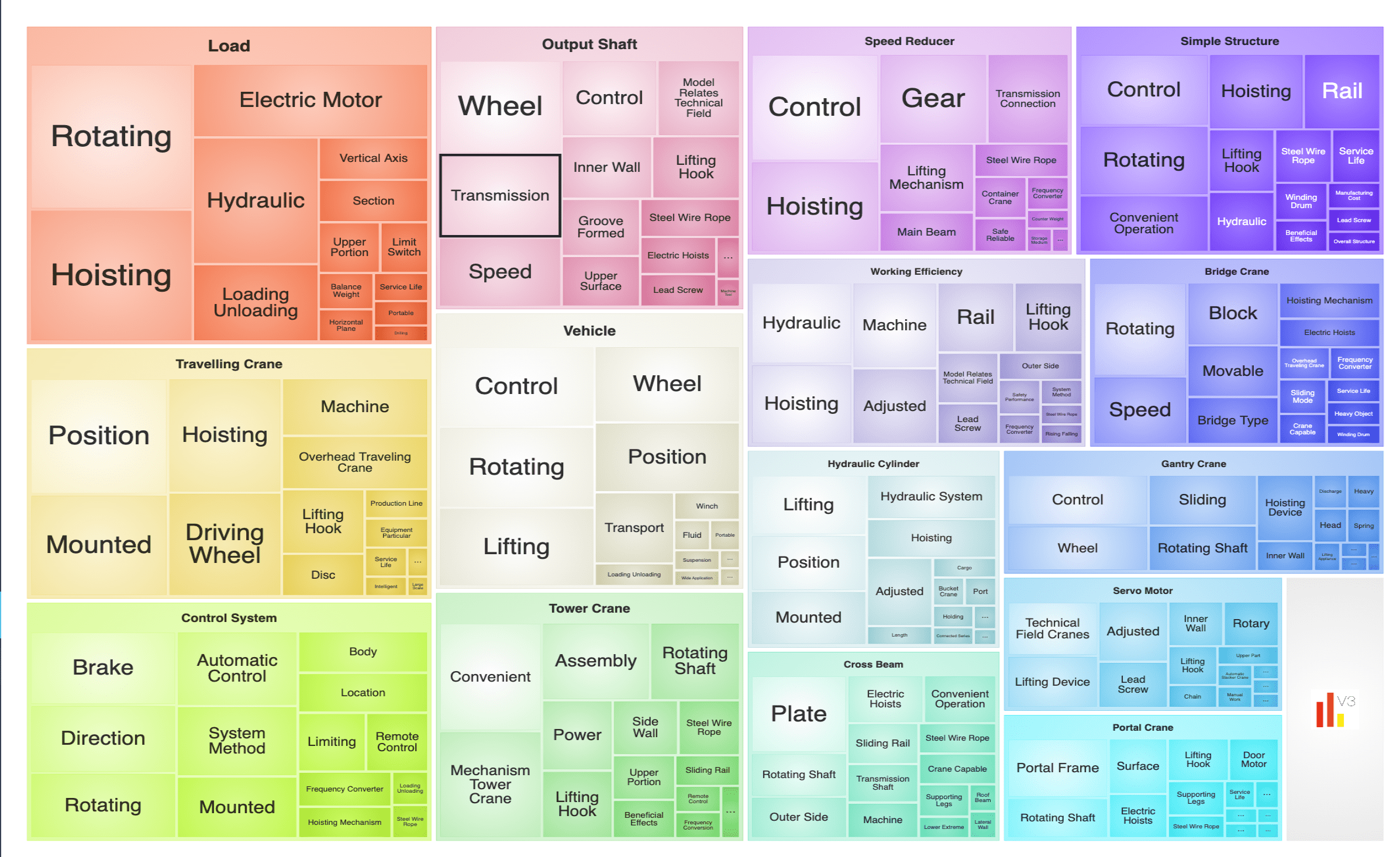
This image an example of semantic mapping taken from our AI-powered patent analytics tool, Minesoft Origin. You can see how the software has used AI to picked out certain terms, grouping them together into semantically-related keyword clusters. This helps R&D and innovation teams to quickly identify the main concepts within certain patents, as well as see how multiple IP properties are related, helping to inform future work. Patbase Analytics also offers something similar with its keyword clustering tool.
Best Practices for Semantic Mapping
Semantic mapping, when executed effectively, can yield valuable insights into patent landscapes and intellectual property assets. To ensure the accuracy, reliability, and usefulness of semantic mapping results, it’s essential to follow best practices throughout the process. Here are some key best practices to consider:
Data Quality & Accuracy
- Ensure the quality and accuracy of the patent data being used for semantic mapping. This includes verifying the correctness of patent metadata, such as publication numbers, titles, abstracts, and classifications.
- Validate the integrity of patent text data, including claims, descriptions, and citations, to minimise errors and inconsistencies in semantic mapping results.
Algorithm Selection
- Select appropriate algorithms and NLP techniques based on the specific objectives of the semantic mapping analysis.
- Consider factors such as the complexity of the patent documents, the size of the patent dataset, and the desired level of granularity in semantic mapping results when choosing algorithms.
Integration with Existing Systems
- Integrate semantic mapping tools and workflows with existing intellectual property (IP) management systems for seamless data exchange and workflow integration.
- Ensure compatibility with other tools and platforms used for patent analysis, prior art search, portfolio management, and IP strategy development.
Regular Updates & Refinement
- Regularly update and refine semantic mapping models to adapt to changes in technology landscapes, industry trends, and business priorities.
- Incorporate feedback from users and stakeholders to improve the accuracy and relevance of semantic mapping results over time.
Customisation & Tailoring
- Customise semantic mapping parameters and settings based on the specific requirements and objectives of the analysis.
- Tailor semantic mapping models to reflect the unique characteristics of the target technology domain, industry sector, or patent portfolio.
Validation
- Validate semantic mapping results through rigorous testing, and benchmarking against ground truth datasets or manual expert assessments.
- Conduct sensitivity analyses to assess the robustness and reliability of semantic mapping outcomes across different scenarios and datasets.
Interpretation & Actionability
- Interpret semantic mapping results in the context of broader business objectives, IP strategy goals, and decision-making processes.
- Translate semantic mapping insights into actionable recommendations, strategic initiatives, and operational plans to drive value creation and competitive advantage.
The Future Implications of Machine Learning & NLP
As machine learning and NLP continue to advance, the future implications for semantic mapping in patent analysis are vast. These technologies hold the potential to further enhance the capabilities of semantic mapping, enabling more sophisticated analysis, prediction of future trends, and automation of various IP-related tasks.
By keeping up with these developments and leveraging emerging technologies, companies can continue to refine their IP strategies and maintain a competitive edge in the ever-evolving world of innovation.
In conclusion, semantic mapping is a powerful tool that is reshaping the field of patents and intellectual property management. By leveraging advanced NLP and machine learning techniques, companies can gain valuable insights into patent landscapes, make informed decisions, and drive innovation forward. Incorporating semantic mapping into an IP strategy is essential for organisations looking to navigate the complex landscape of innovation effectively.
Make Semantic Mapping Easy with Minesoft
Navigating the intricate landscape of patents and intellectual property can be challenging, but with the right tools and techniques, it becomes a seamless process. Minesoft offers cutting-edge patent analysis products, such as Minesoft Origin and Patbase, that make semantic mapping and patent tracking easy and efficient. By leveraging Minesoft’s innovative solutions, users can unlock the power of semantic mapping to gain valuable insights into patent landscapes, identify trends, and make informed decisions to guide their IP strategies. Discover how Minesoft can transform your patent analysis processes by requesting a demo today.